Expression profile of circular RNAs in placentas of women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Huiyan Wang, Guangtong She, Wenbai Zhou, Kezhuo Liu, Jun Miao, Bin Yu
Author information
Keywords: Gestational diabetes mellitus, CircRNA, RNA sequencing, MicroRNA, Placenta
JOURNALS FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
2019 Volume 66 Issue 5 Pages 431-441
DOI https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ18-0291
Browse "Advance Publication" version.
Details
Full Text-HTML
Download PDF (1881K)
Download Meta
RIS
(compatible with EndNote, Reference Manager, ProCite, RefWorks)
BIB TEX
(compatible with BibDesk, LaTeX)
Text
How to download Meta
Contact us
Article overview
Abstract
References (39)
Figures (4)
Information related to the author
Share
Abstract
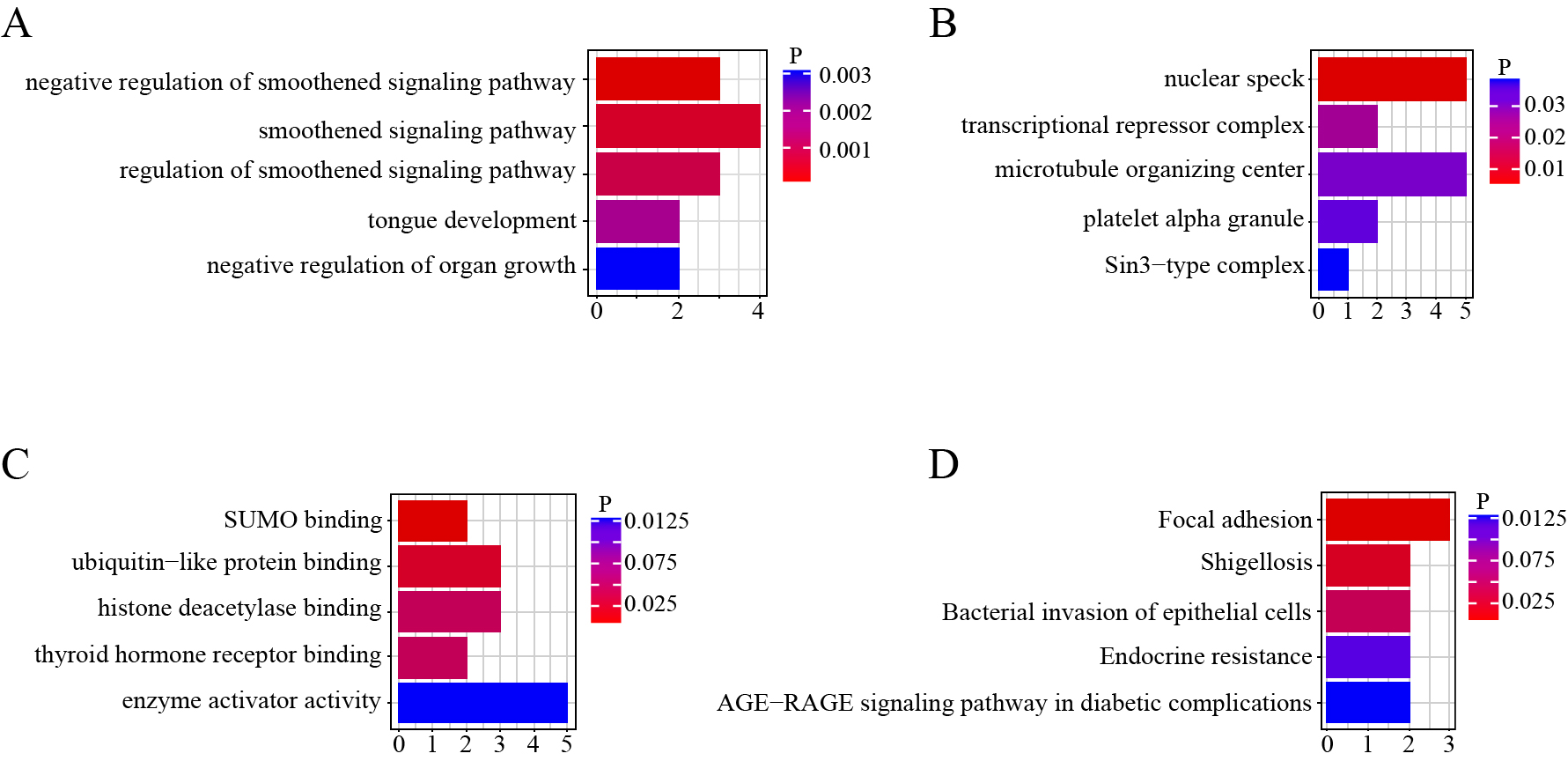
Forty-five pregnant women who underwent cesarean section, including 30 cases of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and 15 normal pregnant women, were enrolled in this study to examine the differential expression of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in the placentas of women with GDM by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis. The differentially expressed circRNAs were analyzed bioinformatically using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment and circRNA-microRNA (miRNA) interaction prediction. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to verify the results. A total of 8,321 circRNAs were identified in the human placenta, among which 46 were differentially expressed (fold change ≥2 and p < 0.05), including three that were upregulated and 43 that were downregulated. According to the GO and KEGG enrichment results, these circRNAs may be associated with vital biological processes, cellular components, molecular functions, and signaling pathways. In particular, KEGG analysis shown they may be involved in advanced glycation end products-receptor for advanced glycation end products (AGE-RAGE) signaling pathway in diabetic complications, indicating that these circRNAs might participate in the occurrence and pathogenesis of GDM. qRT-PCR verified that the expression of circ_5824, circ_3636, and circ_0395 was consistent with RNA-seq analysis; their expression levels were significantly lower in the GDM group than in the control group. The circRNA-miRNA interaction was analyzed according to the molecular sponge mechanism, and its potential function is discussed. These results shed light on future functional studies of circRNAs related to GDM.
References (39)
1 Jovanovic L, Pettitt DJ (2001) Gestational diabetes mellitus. JAMA 286: 2516–2518.
2 Reece EA, Leguizamón G, Wiznitzer A (2009) Gestational diabetes: the need for a common ground. Lancet 373: 1789–1797.
3 Shaat N, Groop L (2007) Genetics of gestational diabetes mellitus. Curr Med Chem 14: 569–583.
4 Mastrogiannis DS, Spiliopoulos M, Mulla W, Homko CJ (2009) Insulin resistance: the possible link between gestational diabetes mellitus and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Curr Diab Rep 9: 296–302.
5 Ilekis JV, Tsilou E, Fisher S, Abrahams VM, Soares MJ, et al. (2016) Placental origins of adverse pregnancy outcomes: potential molecular targets: an Executive Workshop Summary of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Am J Obstet Gynecol 215: S1–S46.
Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου