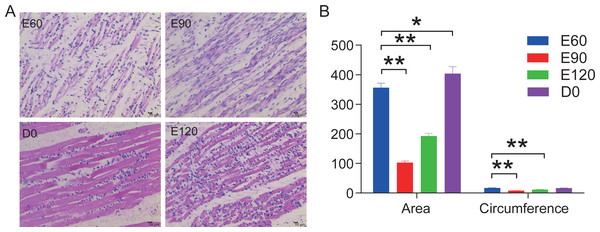
The sheep is an economically important animal, and there is currently a major focus on improving its meat quality through breeding. There are variations in the growth regulation mechanisms of different sheep breeds, making fundamental research on skeletal muscle growth essential in understanding the regulation of (thus far) unknown genes. Skeletal muscle development is a complex biological process regulated by numerous genes and non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). In this study, we used deep sequencing data from sheep longissimus dorsi (LD) muscles sampled at day 60, 90, and 120 of gestation, as well as at day 0 and 360 following birth, to identify and examine the lncRNA and miRNA temporal expression profiles that regulate sheep skeletal myogenesis. We stained LD muscles using histological sections to analyse the area and circumference of muscle fibers from the embryonic to postnatal development stages. Our results showed that embryonic skeletal muscle growth can be characterized by time. We obtained a total of 694 different lncRNAs and compared the differential expression between the E60 vs. E90, E90 vs. E120, E120 vs. D0, and D0 vs. D360 lncRNA and gene samples. Of the total 701 known sheep miRNAs we detected, the following showed a wide range of expression during the embryonic stage: miR-2387, miR-105, miR-767, miR-432, and miR-433. We propose that the detected lncRNA expression was time-specific during the gestational and postnatal stages. GO and KEGG analyses of the genes targeted by different miRNAs and lncRNAs revealed that these significantly enriched processes and pathways were consistent with skeletal muscle development over time across all sampled stages. We found four visual lncRNA–gene regulatory networks that can be used to explore the function of lncRNAs in sheep and may be valuable in helping improve muscle growth. This study also describes the function of several lncRNAs that interact with miRNAs to regulate myogenic differentiation.
Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου