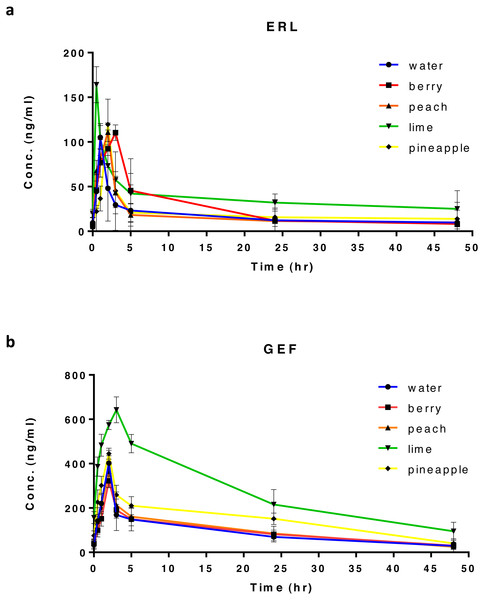
Background Erlotinib (ERL) and Gefitinib (GEF) are considered first line therapy for the management of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). Like other tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), ERL and GEF are mainly metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) CYP3A4 isoform and are substrates for transporter proteins with marked inter-/intra-individual pharmacokinetic (PK) variability. Therefore, ERL and GEF are candidates for drug-drug and food-drug interactions with a consequent effect on drug exposure and/or drug-related toxicities. In recent years, the consumption of flavoured water (FW) has gained in popularity. Among multiple ingredients, fruit extracts, which might constitute bioactive flavonoids, can possess an inhibitory effect on the CYP450 enzymes or transporter proteins. Therefore, in this study we investigated the effects of different types of FW on the PK parameters of ERL and GEF in Wistar rats. Methods ERL and GEF PK parameters in different groups of rats after four weeks consumption of different flavours of FW, namely berry, peach, lime, and pineapple, were determined from plasma drug concentrations using ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Results Data indicated that tested FWs altered the PK parameters of both ERL and GEF differently. Lime water had the highest impact on most of ERL and GEF PK parameters, with a significant increase in Cmax (95% for ERL, 58% for GEF), AUC0–48 (111% for ERL, 203% for GEF), and AUC0–∞ (200% for ERL, 203% for GEF), along with a significant decrease in the apparent oral clearance of both drugs (65% for ERL, 67% for GEF). The order by which FW affected the PK parameters for ERL and GEF was as follows: lime > pineapple > berry > peach. Conclusion The present study indicates that drinking FW could be of significance in rats receiving ERL or GEF. Our results indicate that the alteration in PKs was mostly recorded with lime, resulting in an enhanced bioavailability, and reduced apparent oral clearance of the drugs. Peach FW had a minimum effect on the PK parameters of ERL and no significant effect on GEF PKs. Accordingly, it might be of clinical importance to evaluate the PK parameters of ERL and GEF in human subjects who consume FW while receiving therapy.
Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου