| Photochemistry and Photobiology Volume 95, Issue 4Pages: 909-1093 July/August 2019 |
Issue Information
Research Articles



 Open Access
Open Access








 Open Access
Open Access


Research Articles
Photostability of Terbinafine Under UVA Irradiation: The Effect of UV Absorbers
Pages: 911-923 | First Published: 22 December 2018

In‐depth investigation of the photostability of terbinafine was conducted, taking into account the presence of UV absorbers such as TiO2, ZnO, avobenzone, 3‐(4‐methylbenzylidene)
Efficient Photooxidation of Aryl(hetaryl)pyrazolines by Benzoquinone
Pages: 924-930 | First Published: 06 January 2019
NLOphoric Triphenylamine Derived Donor‐π‐Acceptor‐π‐Donor Based Colorants: Synthesis, Spectroscopic, Density Functional Theory and Z‐scan Studies
Pages: 931-945 | First Published: 28 January 2019

Three dyes (5a‐c) with D‐π‐A‐π‐D structural motif were synthesized and investigated for their photophysical and nonlinear optical behavior. The photophysical behavior of 5a‐c were affected by the polarity of the medium and hence showed solvatochromism. The linear and non‐linear optical properties of the dyes obtained using the spectroscopic and computational methods were affected by different N‐substituted secondary donors used and the polarity of the solvent. The magnitude of nonlinear absorption coefficient (β), the magnitude of nonlinear refraction (n2) and third order nonlinear susceptibility (X(3)) for the dyes were estimated from the Z‐scan analysis.
Photo‐Modification of Melanin by a Mid‐infrared Free‐electron Laser
Pages: 946-950 | First Published: 05 January 2019

We applied a free‐electron laser tuned to mid‐infrared wavelength (5.8 μm) to irradiate melanin. The melanin powder was dispersed by the pulse irradiation with power energy of 500 mJ cm−2, and the minimum pulse number for damage to the morphology of melanin was 2 macro‐pulses, which was equivalent to 1.4 s of irradiation. Analyses by mass spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, and 13C‐nuclear magnetic resonance implied that pyrrole group in the structure of synthetic melanin was dissociated by the FEL irradiation. In addition, melanoma cells were substantially damaged by FEL irradiation.
A Cyanine Photooxidation/β‐Elimination Sequence Enables Near‐infrared Uncaging of Aryl Amine Payloads
Pages: 951-958 | First Published: 30 January 2019
 Open Access
Open AccessRedshifted and Near‐infrared Active Analog Pigments Based upon Archaerhodopsin‐3
Pages: 959-968 | First Published: 12 March 2019

The proton pump archaerhodopsin‐3 (AR3) is widely used in optogenetics as a silencer of neural activity or as a fluorescent indicator of transmembrane potential. In this research, we utilize analogs of its native chromophore all‐trans retinal to generate variants of AR3 and a single mutant. One analog from this study generated redshifted AR3 pigments which could be activated by near‐infrared light. Furthermore, these pigments showed strongly enhanced fluorescence with an emission band in the near‐infrared. We anticipate that these analog AR3 pigments have potential for exploiting near‐infrared light in several optogenetic and bioenergy‐based applications.
UV‐Vis Spectroscopy Reveals a Correlation Between Y263 and BV Protonation States in Bacteriophytochromes
Pages: 969-979 | First Published: 06 March 2019

Biliverdin (grey) and Y263 (teal) undergo parallel deprotonation events, requiring a four‐pKa model to describe the pH‐induced transition. Biliverdin and tyrosine each have two pKas due to reciprocal stabilization of the charges (positive for biliverdin and negative for Y263) that occurs within a selective pH range.
Two Consecutive Polar Amino Acids at the End of Helix E are Important for Fast Turnover of the Archaerhodopsin Photocycle
Pages: 980-989 | First Published: 12 December 2018

Threonine 164 (T164) and serine 165 (S165) residues of the archaerhodopsin (AR) from Halorubrum sp. ejinoor (HeAR) are fully conserved in ARs and are likely involved in a hydrogen‐bonding network at the end of the helix E where most microbial rhodopsins assume a “bent structure” as shown in blue box of the upper left image of AR2. Replacements of these two amino acid residues cause profound change to HeAR photocycle suggesting the involvement of the two amino acid residues in the photoreaction pathway despite they are far from the photoactive center.
Differential Photosynthetic Response of a Green Tide Alga Ulva linza to Ultraviolet Radiation, Under Short‐ and Long‐term Ocean Acidification Regimes
Pages: 990-998 | First Published: 12 January 2019

We investigate the response of Ulva linza to UV radiation in the form of photosynthetically active radiation or PAB radiation. Radiation exposures were assessed following long‐term and short‐term OA treatments. Results showed that increased CO2 decreased the damage and repair rate of thalli grown under short‐term OA conditions with PAB treatment. In thalli, k was increased following PAB treatment at long‐term OA conditions. These results show that blooming algae may be more sensitive to UV radiation in marine environments, but it can develop effective mechanisms to offset the negative effects, reflecting acclimation to long‐term OA conditions.
Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation (UV‐A+UV‐B) on the Antioxidant Metabolism of the Red Macroalga Species Acanthophora spicifera (Rhodophyta, Ceramiales) From Different Salinity and Nutrient Conditions
Pages: 999-1009 | First Published: 27 February 2019

Two algal populations of Acanthophora spicifera adapted to different abiotic conditions were exposed to UV‐A+UV‐B for 7 days (3 hours per day), followed by metabolic analyses, for evaluated the antioxidant responses. Chlorophyll a, phycobiliproteins, carotenoids, mycosporins, polyphenolics and antioxidant enzymes (catalase, superoxide dismutase and guaiacol peroxidase) were evaluated. The present study demonstrates that UVR triggers antioxidant activity in the A. spicifera. However, such activation resulted in greater responses in samples of the point 1, with lower salinity and highest concentration of nutrients.
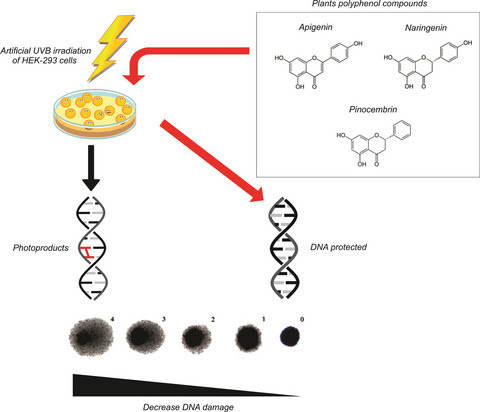
Photoprotective and Antigenotoxic Effects of the Flavonoids Apigenin, Naringenin and Pinocembrin
Pages: 1010-1018 | First Published: 12 January 2019
Bystander Me45 Melanoma Cells Increase Damaging Effect in UVC‐irradiated Cells
Pages: 1019-1028 | First Published: 04 January 2019

The present studies were focused on response of malignant melanoma Me45 cells to UVC radiation and to bystander signals in coculture system. Changes in nonirradiated cells revealed as reduced clonogenic survival, apoptosis and premature senescence. In a feedback response, bystander cells caused increase of damaging effect in directly UVC exposed cells that elicited as decrease of clonogenic cells survival and increase of apoptosis (“reverse damaging bystander effect”). The superoxide, NO and TGF‐β generated in and secreted by bystander cells seem to be engaged in this processes. Pretreatment of bystander cells with inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase blocks reverse signaling.
Cutaneous Photoprotective Activity of a Short‐term Ingestion of High‐Flavanol Cocoa: A Nutritional Intervention Study
Pages: 1029-1034 | First Published: 20 January 2019

In vivo and in vitro studies have shown that prolonged oral administration of flavanol‐rich cocoas extracts have photoprotective effects. We demonstrated that one‐week administration of 4–6 g of a new variety of naturally selected cocoa extract, rich in bioactive compounds, retains a dose‐dependent photoprotective effect. This extract induced a statistically significant increase in the visual erythema threshold and a significant reduction in the “a” parameter. These results are also indicative of the fact that topical sunscreens could be supplemented by a specific diet.
Effect of Titanium Dioxide Film Thickness on Photocatalytic and Bactericidal Activities Against Listeria monocytogenes
Pages: 1035-1044 | First Published: 28 December 2018

The photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin layers increases according to TiO2film thickness to a threshold value close to 400 nm. The film thickness also influences positively the antibacterial activity even though the two strains of Listeria monocytogenes (Lm ScottA and Lm ECL 136) showed different sensitivity to TiO2 photocatalysis.
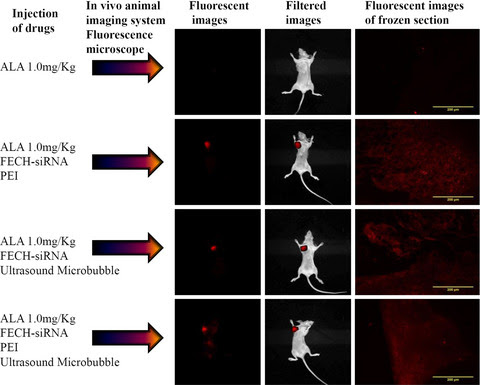
Comparative Study of the Effects of Ferrochelatase‐siRNA Transfection Mediated by Ultrasound Microbubbles and Polyethyleneimine in Combination with Low‐dose ALA to Enhance PpIX Accumulation in Human Endometrial Cancer Xenograft Nude Mice Models
Pages: 1045-1051 | First Published: 24 December 2018

Red fluorescence caused by the accumulation of PpIX in endometrial cancer xenografts in nude mice after high‐dose ALA injection could be detected easily by in vivo animal imaging system, but low‐dose ALA (1.0 mg kg−1) was injected into xenografts, there was no red fluorescence of tumor. However, knockdown of FECH in nude mice was performed by transfection with FECH‐siRNA mediated by PEI and ultrasound microbubbles alone or in combination, then 1.0 mg kg−1 ALA was injected, apparent red fluorescence of the xenografts was observed, and the fluorescence intensity was PEI+ ultrasound microbubbles > PEI >
Ferrochelatase Deficiency Abrogated the Enhancement of Aminolevulinic Acid‐mediated Protoporphyrin IX by Iron Chelator Deferoxamine
Pages: 1052-1059 | First Published: 15 February 2019
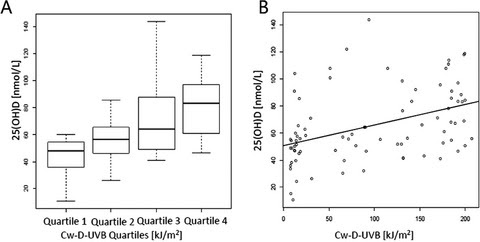
Sunshine is an Important Determinant of Vitamin D Status Even Among High‐dose Supplement Users: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial in Crohn's Disease Patients
Pages: 1060-1067 | First Published: 16 January 2019

The aim of this study was to examine contribution of sunshine and supplementation to vitamin status. Participants were randomized to 2000 IU day−1 of vitamin D3 or placebo for 1 year, with 25‐hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) being measured every four months. Based on participant's place of residence, daily ambient UVB dose (D‐UVB) was obtained. Cumulative and weighted ambient UVB (cw‐D‐UVB) exposure prior to each blood draw was calculated for each participant. Both supplementation and Cw‐D‐UVB were found to be strongly associated with 25(OH)D. Sunshine is an important determinant of 25(OH)D concentration, even in those who are taking high‐dose vitamin D supplements.
 Open Access
Open AccessInfluence of Air Temperature on the UV Exposure of Different Body Sites Due to Clothing of Young Women During Daily Errands
Pages: 1068-1075 | First Published: 28 January 2019

Clothing is one of the factors influencing personal ultraviolet radiation (UVR) exposure. In this study, clothing habits of young females were investigated in dependence of meteorological conditions. A body chart and a coding scheme were developed to indicate the exposed body sites. Results showed that air temperature is the dominating factor for UVR exposure. With increasing temperature, the first area of the body to be exposed to UVR, aside from face and hands, was the décolleté, followed by nape, ankles, instep and forearms. Observations also indicate that the frequency of people's being outdoors decreases significantly at temperatures higher than 30°C.
Erythemal UV Radiation on Days with Low UV Index Values—an Analysis of Data from the German Solar UV Monitoring Network over a Ten‐year Period
Pages: 1076-1082 | First Published: 15 February 2019

Current WHO guidance for sun exposure on days with Global Solar UV Index (UVI) values of less than 3 does not see any need for sun protection on these days. Contrary to this, our analysis of erythemal irradiance data of such days from the German solar UV monitoring network shows that doses resulting from exposure of only two hours around solar noon can be sufficient to induce erythema in fair‐skinned people on days with UVI values of 2, thereby questioning the WHO claim of harmlessness for this part of the low exposure category of the UVI.



Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου